Face Recognition with Kernel Class Dependent Feature
Analysis using Correlation Filters (Face Recognition
Grand Challenge)
|
|
|
|
|
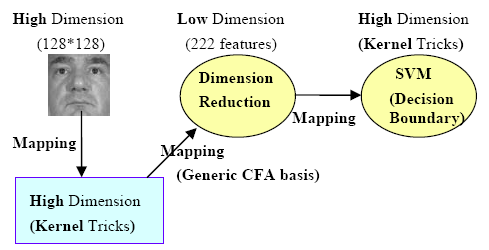
Kernel class-dependent feature analysis (KCFA)
method has been proposed to generalize the
approaches using correlation filters for face
recognition. The dimensionality of the test images
(gallery and probe) is efficiently reduced by
projecting the test images onto the class
specific basis vectors designed from the
generic training set using correlation filters. We
evaluate our proposed algorithm using the Face
Recognition Grand Challenge Dataset showing better
performance over other approaches such as PCA, LDA,
KPCA and KLDA.
|
Visual and Thermal Face
Recognition using Correlation Filters
|
|
|
|
|
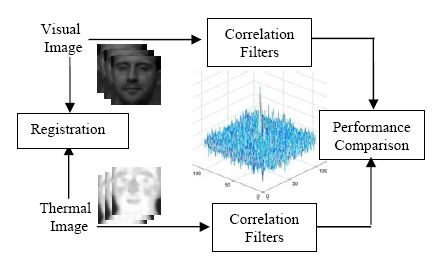
Correlation
filter designs have shown to be distortion invariant and the advantages of
using thermal IR images are due to their invariance to visible illumination variations.
A combined use of
thermal IR image data and
correlation filters makes a viable means
for improving the performance of face recognition
techniques, especially beyond visual spectrum.
|
Face Modeling from Structure From Motion
|
|
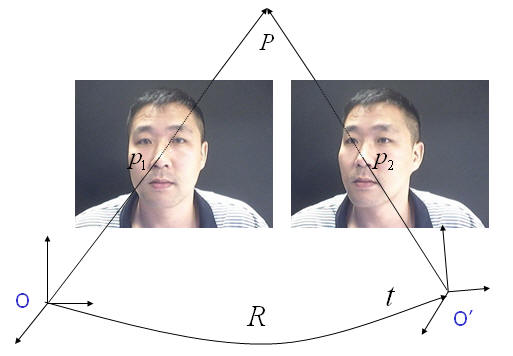
Correspondence Problem for recovering the structure |
|
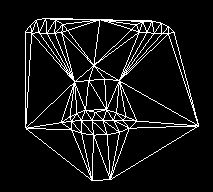 
Recovered Shape and Texture Mapping
|
|
|
|
Structure from Motion (SfM) theory
enables to estimate the 3D shape and the camera
motions as well with images taken different views.
Using m different frames and n correspondence points
across frames, the Factorization Method estimates
camera parameters and 3D shape in the scene with
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) method. The most
challenging part in the SfM is so called the
Correspondence Problem. Researchers have been trying
to track those features using the Kalman Filter and
the Lucas Kanade optical flow algorithm (LK
tracker). Those tracking algorithms easily fail if
the correspondent points not consistent across
frames. Thus more reliable tracking algorithms are
needed to be developed in order to recover 3D faces
in a fully automated way.
|

